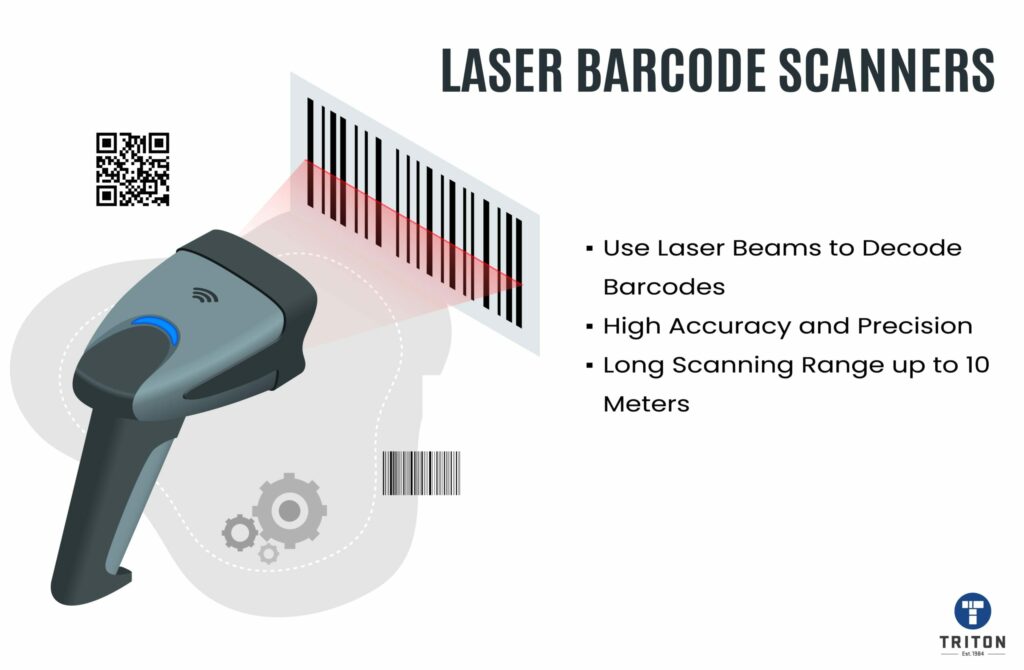
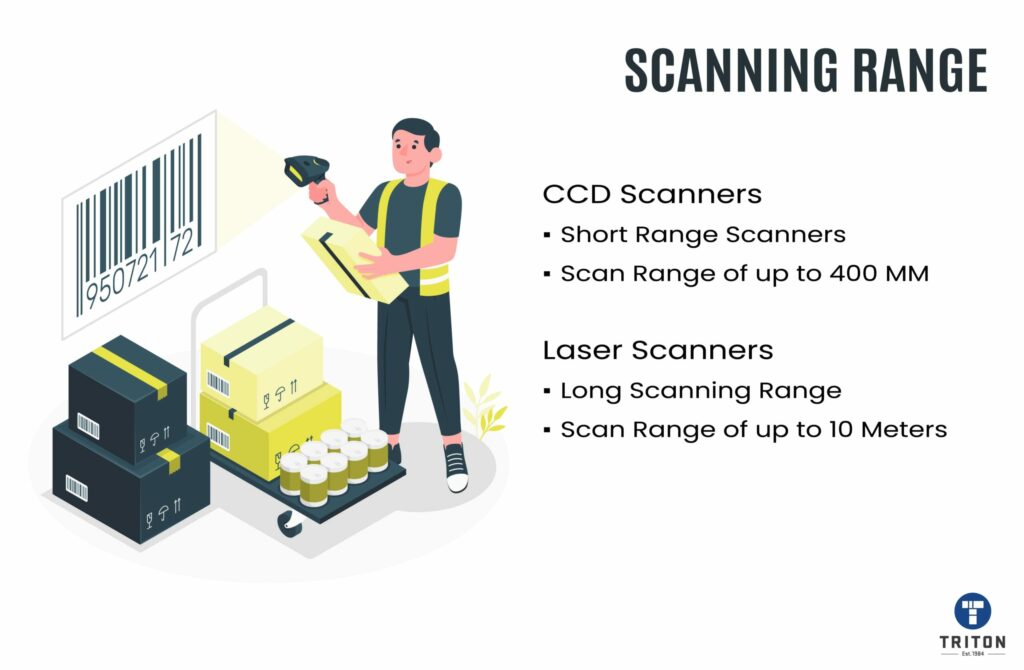
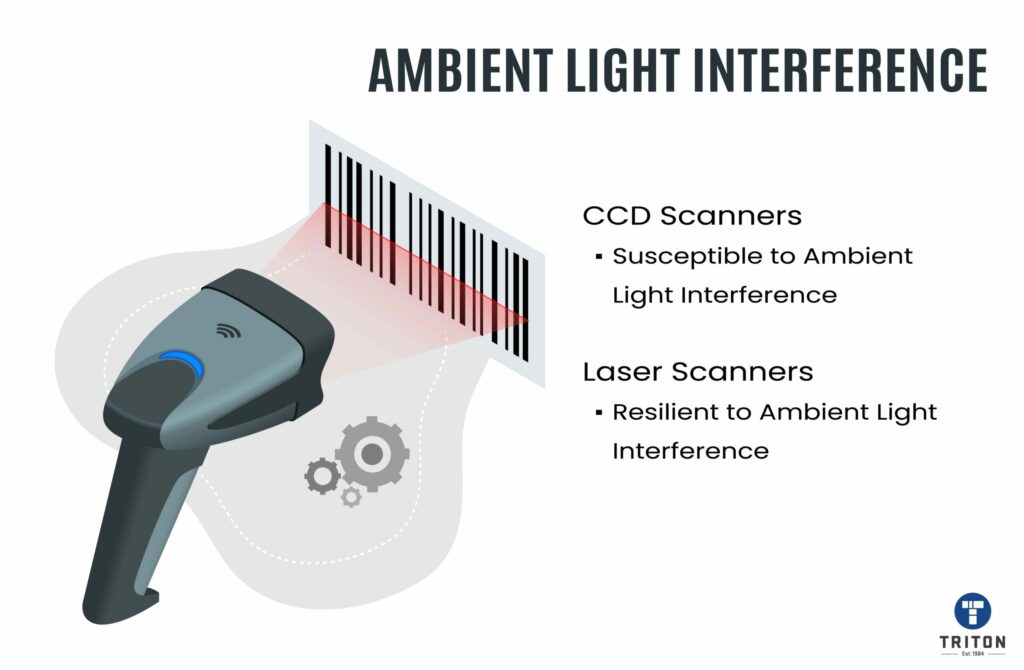
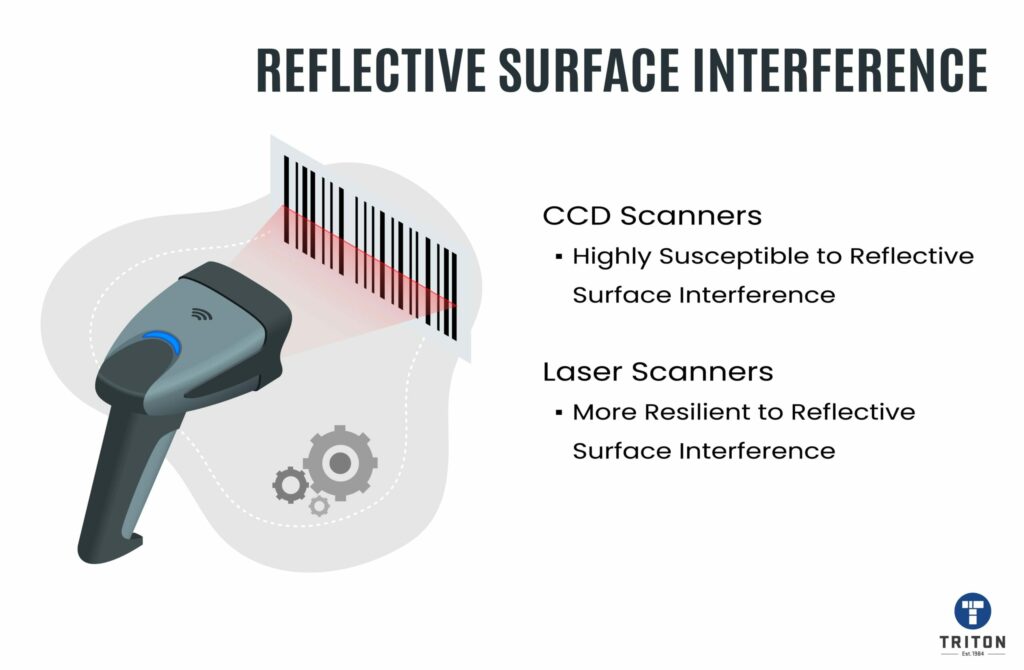
In conclusion, both CCD and laser barcode scanners have their advantages and limitations.
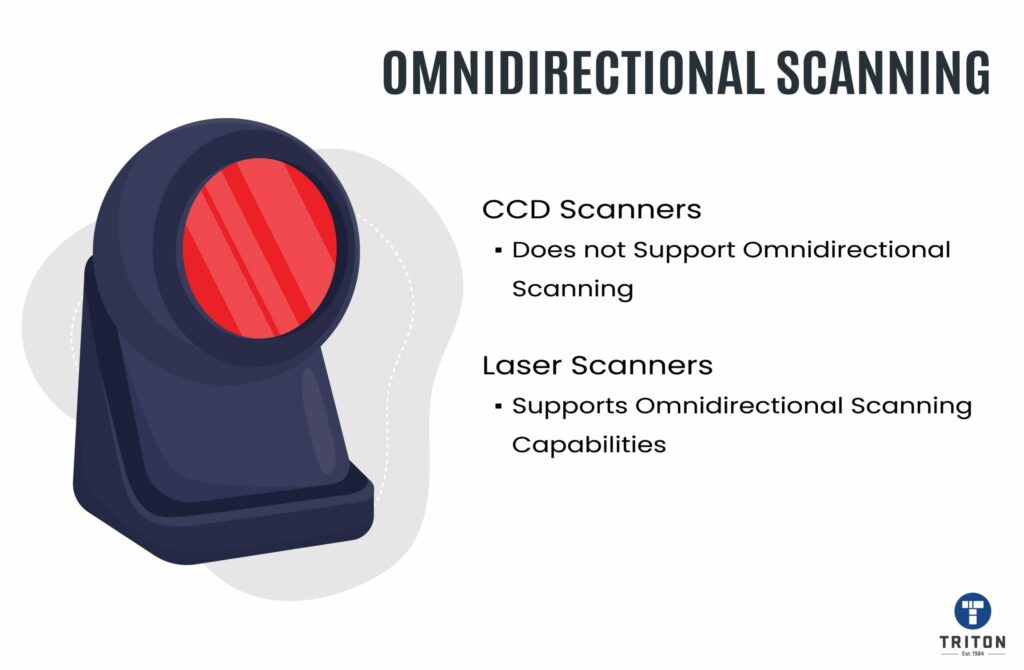
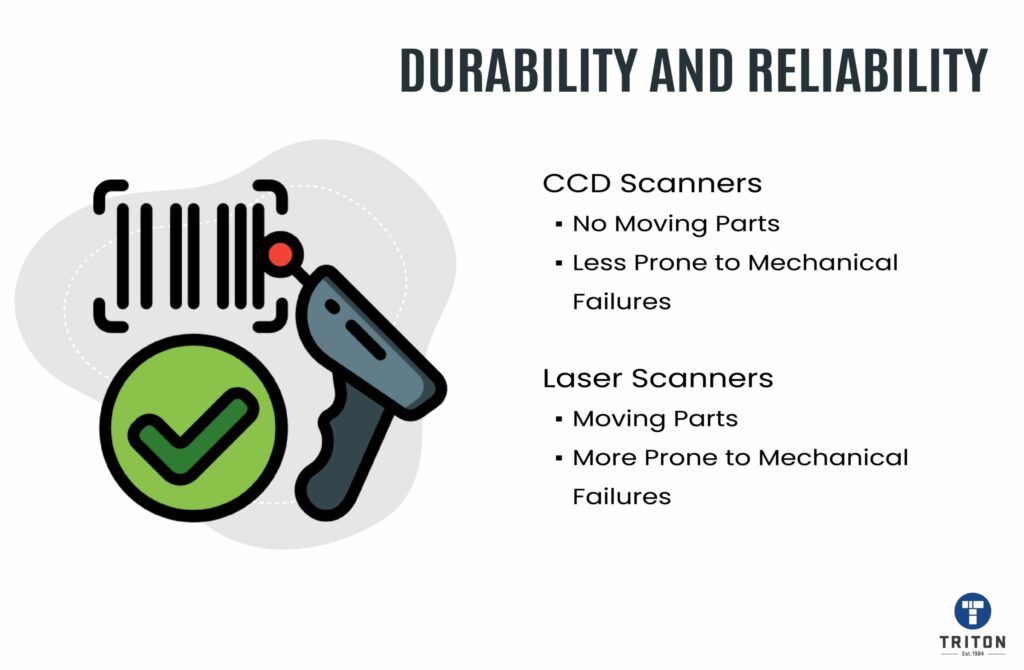
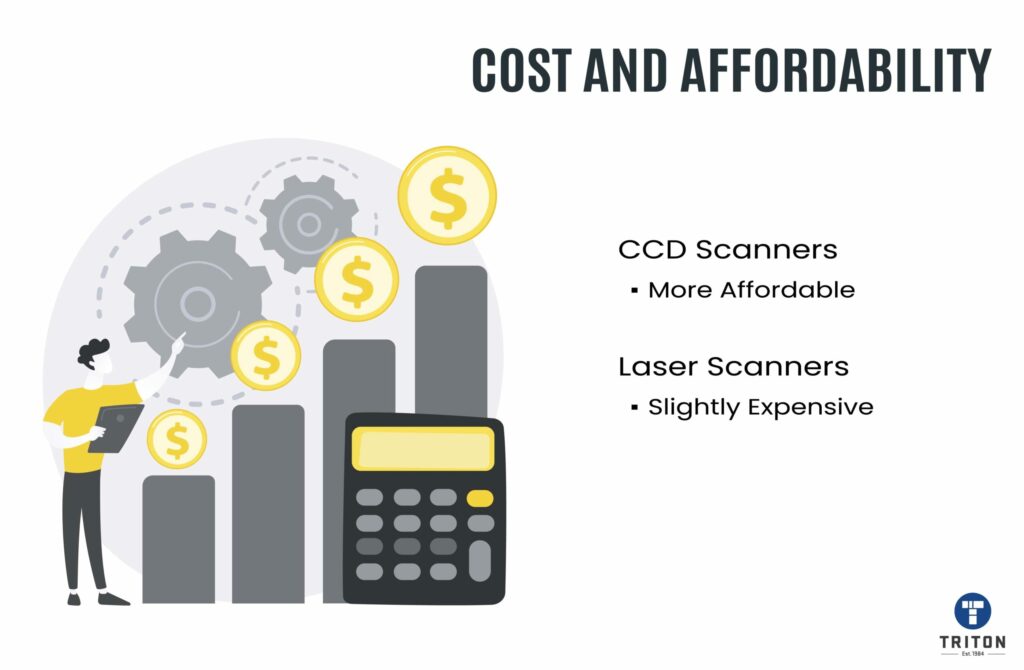
CCD scanners are more durable, affordable, and suitable for occasional scanning, while laser scanners are faster, more versatile, and suitable for high-volume scanning operations.
When choosing a barcode scanner for your business, it is essential to consider your specific business’s needs. Always consider factors such as supported barcode symbols, the ability to scan small barcodes, the volume of scanning, scanning range, required scanning speed, budget and work environment to determine which type of scanner is best suited for your requirements.
Regardless of your choice, having a barcode scanner is essential in today’s business environment. At Triton, we understand the importance of this technology, which is why we are committed to providing our customers with the very best barcode scanners from top brands such as Honeywell and Zebra.
Our range of scanners is diverse and extensive, ensuring that there is a barcode scanner to meet the unique needs of any business. Our collection encompasses USB barcode scanners, general barcode scanners, rugged barcode scanners, fixed scanners & sensors, 2D barcode scanners, mobile terminals, wireless barcode scanners and Bluetooth barcode scanners.
So, why wait? Shop with us and start scanning with ease. For more information about our barcode scanning products, contact us via the live chat widget below.
We look forward to helping you find the perfect barcode scanning solutions for your needs.
Thanks for reading!