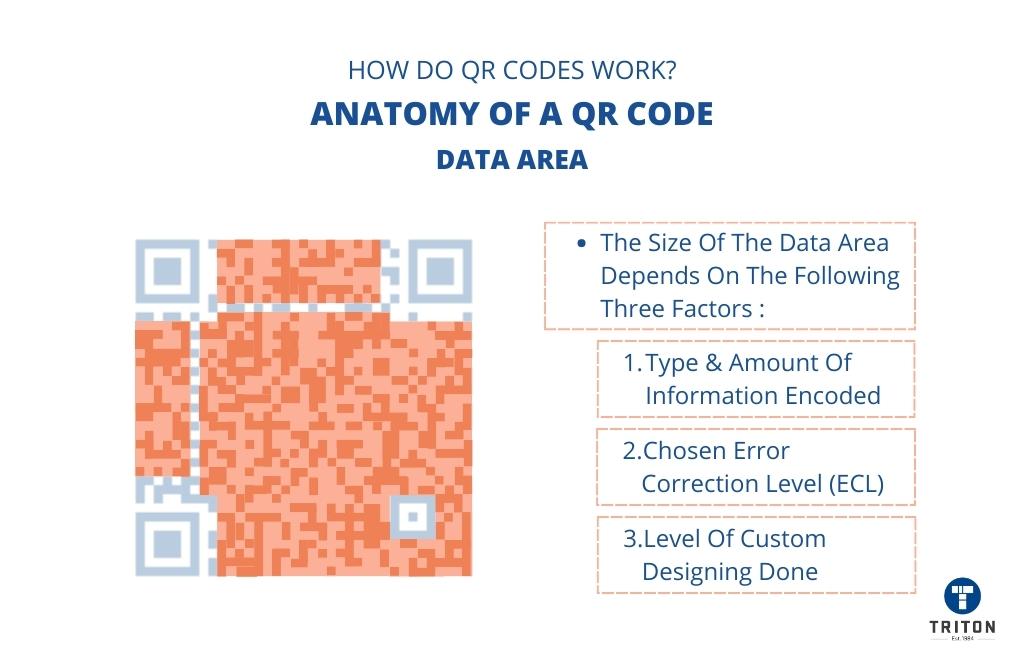
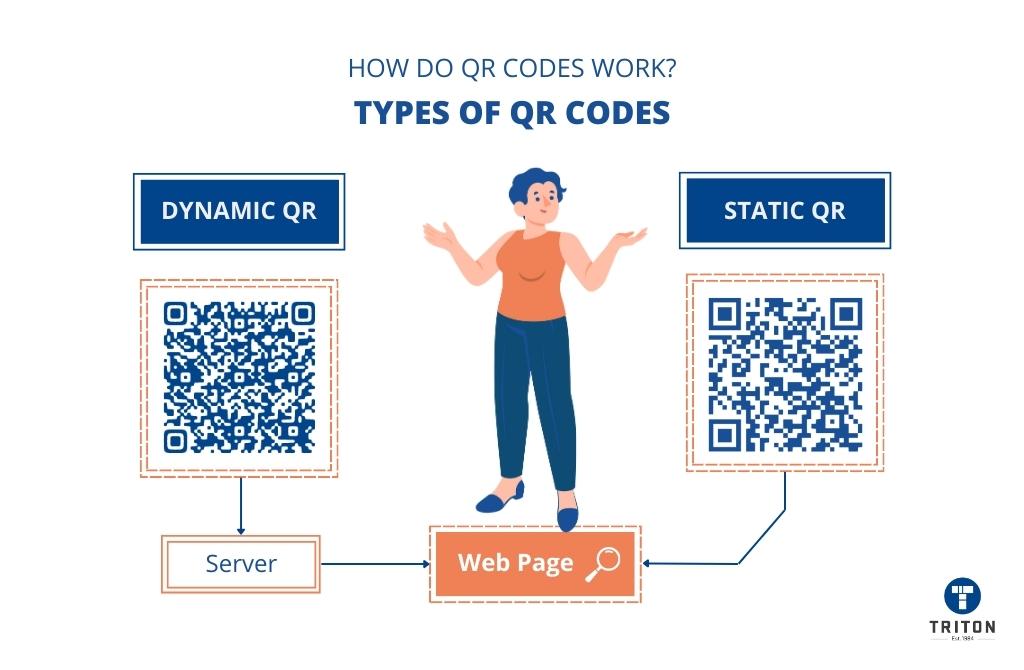
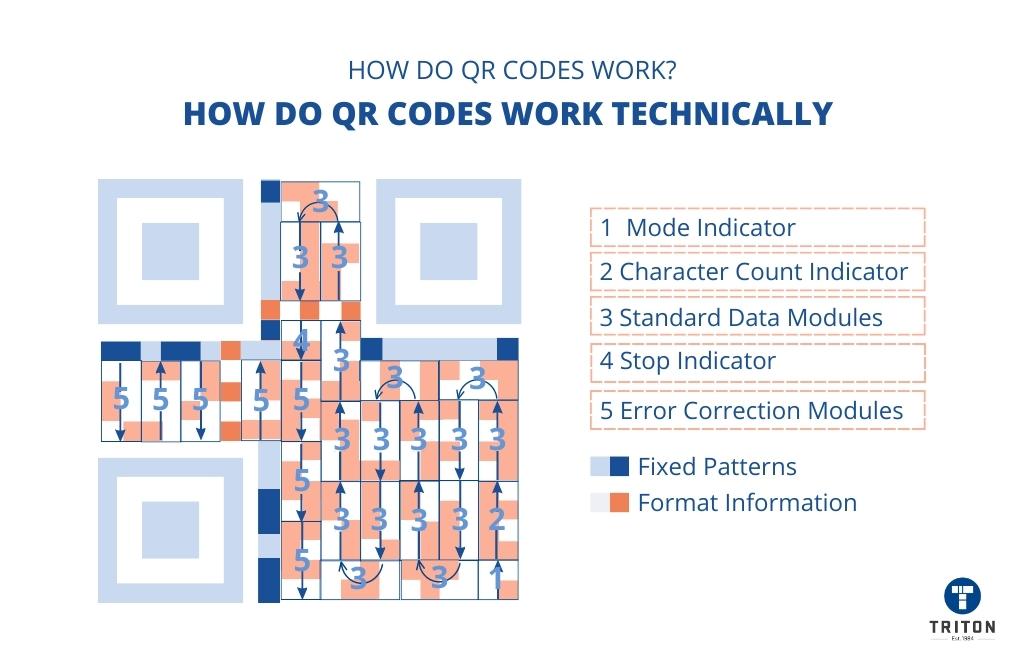
Position Markers
Position markers are the three identical square structures located at the top right, top left, and bottom left corners of the QR codes.
Position markers help mobile devices and QR code scanners to accurately detect the presence, orientation and size of a QR code in an image.