
Thermal paper is a specialised printer paper engineered to change colour when exposed to heat. It is manufactured using heat-reactive dyes and developers.
Thermal paper is widely used in businesses for printing receipts, ATM transactions, shipping labels, etc. Printing on thermal paper is fast, inkless, and cheap.
The thermal paper comprises many layers, including layers with special chemical coating. The chemical coating is primarily made up of leuco dyes and developers.
When subjected to heat from the thermal print head, leuco dyes react with the developers, producing a visible mark on the paper.
This heat-sensitive reaction is the reason behind the clear, smudge-free prints on receipts, tickets, and labels.
The efficiency and precision of thermal printing have made thermal paper a vital tool in various sectors, ensuring quick, cheap, and reliable prints. Refer to our article on how does thermal printers work to understand thoroughly.
Triton is your ultimate destination for all your thermal printing needs. We’ve meticulously curated a premium collection that features state-of-the-art thermal printers sourced from industry titans like Epson, Element, Senor, Honeywell, Zebra and TSC. Additionally, we offer a range of coloured label printers from OKI, ensuring a diverse selection to cater to your specific requirements.
Our inventory spans a wide spectrum of thermal printers, encompassing direct thermal printers, thermal transfer printers, barcode label printers, desktop printers, industrial printers, mobile printers and receipt printers. We’re your one-stop solution for every thermal printing need you may have.
But that’s not all.
At Triton Store, we recognise the importance of keeping your printers in top-notch condition. That’s why we provide an extensive array of spare printer parts and accessories, waterproof printer enclosures, cables and cleaning wipes to ensure your printers stay operational. You’ll also find premium thermal print heads from renowned brands like Zebra, Honeywell, TSC, Intermec, Datamax, SATO, and Bizerba, all designed to optimise your printer’s performance.
What sets us apart is our commitment to offering superior products at unbeatable prices. Our dedicated team of customer service experts is just a click away, ready to assist with any inquiries or issues you may have. Connect with us through the live chat widget below to experience exceptional service and find the perfect solutions for your printing needs.
Thermal paper is more than just paper; it combines science and engineering. Let’s delve into what sets thermal paper apart from your everyday sheet.
Heat sensitivity is a defining feature of thermal paper. When exposed to the heat from a thermal printer’s printhead, the paper produces clear, smudge-free images. This makes thermal printing highly efficient for quick and clean printing tasks.
Thermal papers have a smooth surface. A smooth surface guarantees high-definition prints, offering clarity and precision in the final output. This quality is essential in applications where accuracy and legible printing are important.
Printing labels with thermal papers is way cheaper than laser printers and inkjet printers.
Inkjet printers can cost between 5 to 10 cents per page, whereas laser printers can cost between 2 to 4 cents per page. In comparison, a thermal printer can produce millions of labels with one printhead at the cost of 1 to 3 cents per label.
Thermal printers are also faster at printing labels than other types of printers. For example, a mid-range thermal printer can print at a speed of 8 inches (~200 mm) per second.
Explore our informative guides to compare a thermal printer with a laser printer and a inkjet printer
Versatility is a hallmark of thermal paper. It’s suitable for a broad spectrum of applications, from printing shipping labels to lottery tickets.
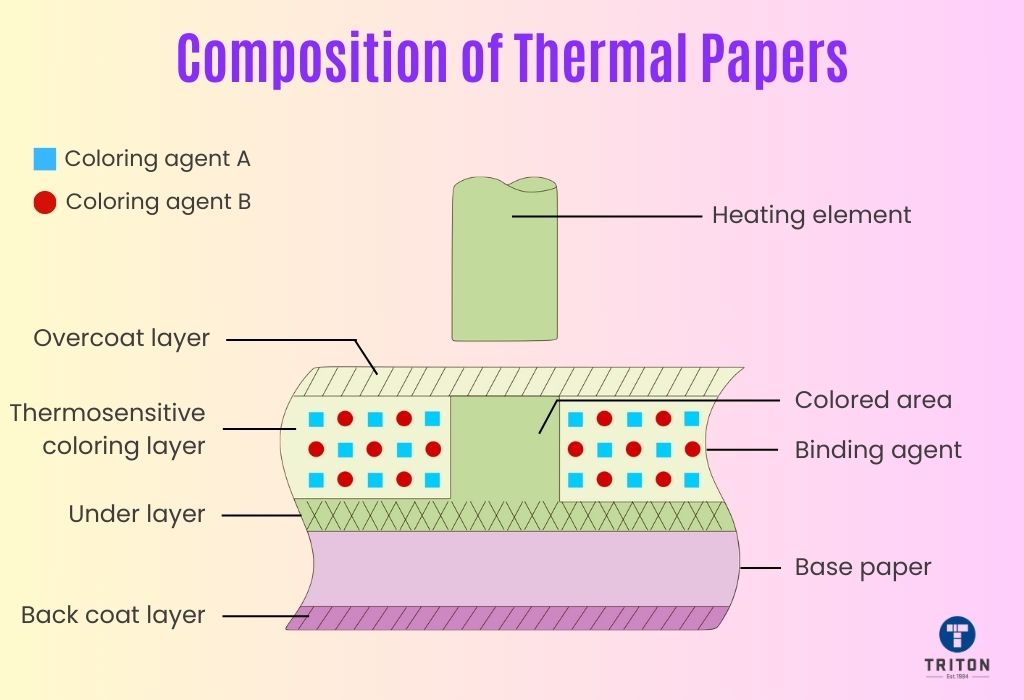
Thermal paper combines carefully chosen layers, each serving a specific purpose. This thermal layer composition ensures the paper’s unique heat-reactive properties.
Let’s explore the key components that make up the thermal paper structure.
The base paper is the substrate or the foundation for other layers.
The base paper, typically made from wood pulp, serves as the starting point for thermal paper. It’s primed with a precoat to fill any pores, ensuring a smooth and even printing surface. Synthetic thermal stocks are also an option.
This foundational layer is crucial for the paper’s durability, heat insulation, image clarity, and overall performance. In short, the base paper sets the stage for reliable, high-quality prints.
The precoat layer (also known as undercoating) is an integral part of thermal printing paper. It sits between the base paper and the thermal coating.
Its main function is to smooth the surface of the base paper, ensuring the thermal coating is applied evenly. This application is vital for producing clear images when the paper reacts to heat.
Additionally, the precoat layer helps the thermal coating adhere better to the paper, improving print quality. It also protects the thermal printer paper, helping maintain its quality over time. In short, the precoat layer ensures the thermal paper functions effectively and produces consistent results.
The thermal coat is the defining layer of the thermal paper roll, enabling its unique heat-sensitive reactions. This coat is chemically formulated to change colour when subjected to heat. As thermal paper runs through a thermal printer, the printer’s heat activates the chemicals in this layer, resulting in the appearance of text or images.
The thermal coat comprises of the following;
Initially colourless, leuco dyes change colour when exposed to heat and developers. This reaction is the cornerstone of the visible print on thermal paper.
These chemicals activate leuco dyes upon heating, resulting in the clear, visible print commonly seen on items like receipts.
Sensitisers fine-tune the paper’s heat responsiveness, ensuring compatibility with the specific temperature range of the designated printer.
Stabilisers maintain the print’s integrity over time, preventing quick fading and prolonging the life of the printed image.
Thermal paper doesn’t just stop at the primary thermal coat. To enhance its functionality and durability, additional coatings can be applied.
The topcoat is applied to the front of the thermal paper to protect the printed image. It helps prevent smudging and fading, especially when exposed to substances like oils or water.
This is added to the back of the paper. It ensures added durability and protection, especially in conditions where the paper might be handled frequently.
Both coatings enhance the durability and clarity of thermal paper, making it a reliable choice for various uses.
In summary, each component is specialised, collectively contributing to the paper’s unique thermal printing capabilities.

The table created below gives you an idea about the types of Thermal Paper.
Paper Type | Description |
|---|---|
Direct Thermal Paper
| Direct Thermal Paper is a type that utilises chemicals that react to heat, producing an image. It’s commonly chosen for printing receipts and labels meant for short-term use. One of its notable features is that it doesn’t require ribbons or ink for printing.
|
Thermal Transfer Paper
| Thermal Transfer Paper operates differently. It relies on a heated ribbon to transfer ink onto the paper, making it suitable for creating durable labels that can withstand various environmental factors. For this type, a ribbon is essential during the printing process. This paper caters to requirements for more enduring labels.
|
Refer to our guide on direct thermal vs thermal transfer printers to learn more.
At Triton, we go beyond providing exceptional thermal printers; we offer a comprehensive selection of high-quality print consumables designed to complement and enhance the performance of your thermal printers. Explore our extensive inventory, which includes premium thermal transfer ribbons, thermal labels, thermal carton labels, thermal carcase tags, food-compliant thermal inserts, receipt rolls and shipping & freight labels.
With Triton, you not only get access to top-tier thermal printers but also a complete solution that covers all your printing needs. We are committed to providing excellence in every aspect of your printing experience, from hardware to consumables and software like Seagull Scientific’s BarTender, all backed by our exceptional customer service team. If you have any questions or need assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out via the live chat widget below.
Thermal paper has a unique texture, often smoother than regular paper.
To determine if a paper is thermal, you can use the rub test.
Simply rub the paper’s surface with a fingernail or coin. If it’s thermal paper, a black mark will appear due to the heat-sensitive chemicals reacting to the friction. This quick test is a reliable way to differentiate thermal paper from other types.
Thermal paper’s durability is a frequent query among users. Influenced by various factors, its lifespan ranges from immediate use to several years.
Thermal paper, when stored in a controlled environment, has a shelf life of up to 10 years. However, the actual longevity can vary based on the quality of the paper, the chemicals used in its production, and storage conditions.

Light – Direct exposure to sunlight or fluorescent light can cause the paper to darken, reducing its lifespan.
Heat – Being heat-sensitive, storing thermal paper in a hot environment can trigger colour-changing chemicals, leading to premature darkening.
Contact with Plastics or PVCs – Storing thermal paper in contact with plastic materials, like certain plastic sleeves or wallets, can lead to image deterioration.
Humidity – High humidity can adversely affect the paper’s quality and reduce its lifespan.
Oils and Chemicals – Exposure to oils, solvents, and other chemicals can degrade the paper quality.
To maximise the lifespan of thermal paper, it’s recommended to store it in a dark, cool, and dry environment, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Additionally, keeping it away from plastics, PVCs, and chemicals will help preserve its quality.
Thermal paper, commonly used for receipts, contains Bisphenol A (BPA) as a developer in its heat-sensitive layer. BPA has potential endocrine-disrupting properties, raising health concerns when transferred from paper to skin. However, the amount transferred is minimal, and the health risks are still debated.
To address these concerns, some manufacturers now offer BPA-free thermal paper, using alternatives like Bisphenol S (BPS). While BPS is considered a safer option, its long-term effects remain under study. It’s advisable to wash hands after handling receipts to minimise potential exposure.
Thermal papers are used in a variety of applications, including.
These are just a few examples, but thermal paper’s convenience and cost-effectiveness make it suitable for any application where temporary, legible printing is required.
Some thermal papers contain Bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical that has raised health concerns. BPA can be absorbed through the skin, especially if one has recently used hand sanitisers or lotions. Prolonged exposure to BPA may have an effect on the brain and prostate gland of fetuses, infants, and children.
Yes, in response to health concerns, manufacturers have produced BPA-free thermal papers. However, some alternatives, like Bisphenol S (BPS), might also have health implications.
When stored in a controlled environment, thermal paper can have a shelf life of up to 10 years. However, factors like exposure to light, heat, and humidity can affect its longevity.
While it’s technically possible to recycle thermal paper, the presence of chemicals like BPA can contaminate other recycled products. It’s advisable to check with local recycling guidelines.
Excessive heat or light exposure can trigger the heat-sensitive chemicals in the paper, causing it to darken.
Thermal paper is a specialised type characterised by its unique chemical coating that changes colour upon exposure to heat, resulting in clear and smudge-free prints.
This technology, utilising a mix of leuco dyes, developers, and other chemicals, has greatly impacted sectors like retail, banking, and healthcare by offering quick, high-definition prints without traditional ink.
Its wide range of applications, from everyday receipts to medical records, highlights its importance in our daily routines.
Due to its cost-effectiveness, durability, and speed, thermal paper is a valuable asset in contemporary printing solutions.
Melbourne
Brisbane
Phone 1300 558 438
Live Chat – Widget below
Melbourne
Brisbane
Phone 1300 558 438
Live Chat – Widget below