
Labels play a pivotal role in product packaging, acting as a vital communication bridge between products and consumers. They provide essential information like product details, usage instructions, and legal compliance, contributing significantly to brand identity and influencing customer decisions.
The need for precision and efficiency in both creating and applying these labels has catalysed the evolution and widespread adoption of labelling machines across various industries.
This article aims to demystify labelling machines, breaking down their types, components, and operational principles. Additionally, we will highlight their advantages across various industries and address common queries, providing a thorough insight into the world of labelling machines for those new to the subject.
So put on your learning hat, and let’s get started!
For a comprehensive understanding of labelling and its various aspects, check out our article, What is Labelling?
The term ‘labelling machine’ refers to equipment specifically designed to print and apply labels onto various products, packages, or containers.
Labelling machines come in various forms, each tailored to specific types of labelling tasks and industry requirements. They range from simple, hand-operated devices suitable for small-scale operations to highly sophisticated, automated systems engineered for high-volume production lines. Advanced machines may also include features like barcode scanners, printers for variable information, and inspection systems to ensure label accuracy and quality.
Labelling machines are essentially indispensable in modern packaging processes, offering a blend of precision, efficiency, and adaptability. They cater to various industrial needs, from basic labelling tasks to complex, high-speed applications, underscoring their critical role in product presentation and compliance.
Triton stands at the forefront of labelling technology, offering a comprehensive array of labelling machines that embody the pinnacle of quality and innovation.
Our selection spans from automated weighing and labelling solutions tailored for meat processors and various food packaging lines—such as the Automatic Carton Weigh Labeller and Automatic Weigh Price Applicators—to sophisticated automated label applicators like the Carton Seal Applicator and Print and Apply Applicator.
Additionally, for businesses aiming to adopt more sustainable practices without compromising on speed and efficiency, our Linerless Label Applicators and Linerless Label Banding Machines offer an eco-friendly alternative that ensures products stand out on the shelf.
Triton also caters to manual weight labelling needs with robust solutions like the Carton Weigh Label Station and Price Weight Label and Totalise Station, providing versatile options for processing individual items or bulk packaging.
With Triton, you’re guaranteed the highest levels of service and after-sales support, ensuring your labelling processes are seamless and state-of-the-art. For further details and personalised assistance, please reach out through our live chat widget below. Our team of experts is eager to provide the help you need, ensuring you find the perfect labelling solution for your business.
Different types of labelling machines have been developed to cater to a wide range of products, packaging materials, and operational scales. The diversity in these machines is primarily driven by factors such as the nature of the product being labelled, the type of label required, the volume of production, and the degree of precision and automation needed.
In this section, we have categorised labelling machines into distinct types based on several key criteria. These criteria include.
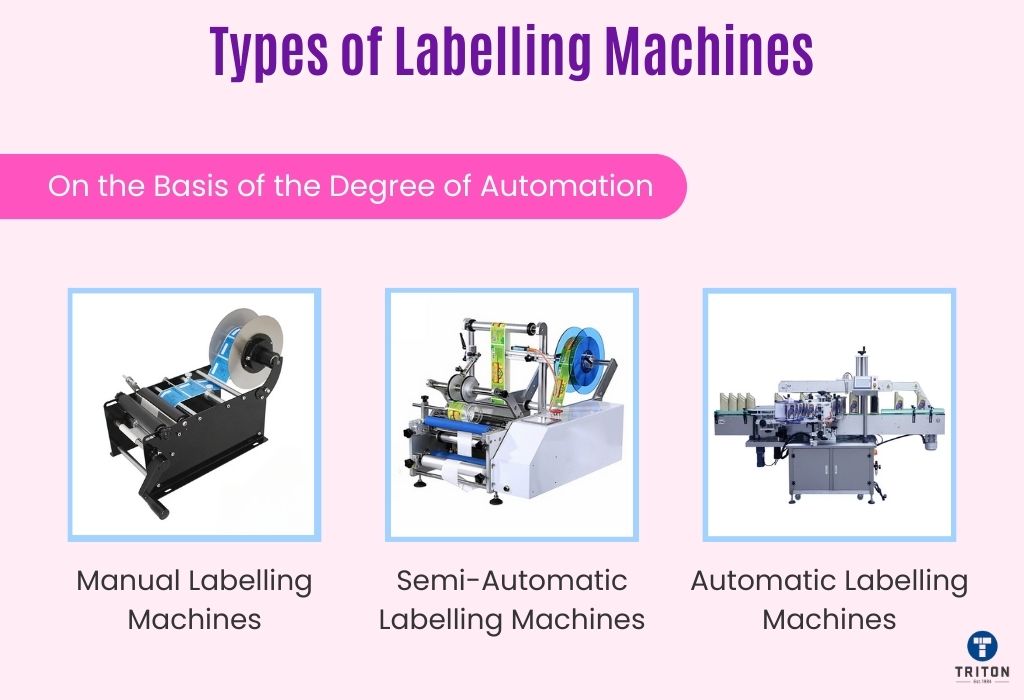
One of the primary ways to differentiate labelling machines is by the degree of automation they offer. This categorisation helps understand the level of manual intervention, speed, and scale of operations each type of machine is best suited for. Below, we explore the three main types: Manual, Semi-Automatic, and Automatic labelling machines.
Manual labelling machines are the most basic form of labelling equipment. They require direct human effort to operate, with an operator manually placing and applying labels to products.
These machines are typically used in small-scale operations where the volume of products is manageable, and the speed of labelling is not a critical factor. They are cost-effective, easy to use, and require minimal maintenance, making them suitable for startups or small businesses.
Manual labelling machines are best suited to label round bottles or jars made of glass or plastic and small boxes.
Semi-automatic labelling machines offer a middle ground between manual and fully automated systems. In these machines, some aspects of the labelling process are automated, but they still require human intervention for certain operations.
In semi-automatic labelling machines, an operator must manually place products into the machine, after which the machine automatically applies the labels. Once the label is applied, the operator again needs to remove the product from the machine.
Semi-automatic labelling machines are ideal for medium-scale operations where higher efficiency is needed, but the investment in fully automated systems is not justifiable.
Automatic labelling machines represent the pinnacle of efficiency and speed in the labelling process. They are designed to handle high volumes of products with minimal human intervention.
Automatic labelling machines automatically dispense, apply, and secure labels onto products, often at high speeds. They have advanced features like conveyor belts, integrated printing systems, and sophisticated control panels.
Automatic labelling machines are essential in large-scale manufacturing environments where speed, consistency, and volume are critical.

The printing technology used in labelling machines significantly influences their application and efficiency. Different printing methods cater to varying label requirements, such as durability, clarity, and the ability to print variable information. Here, we explore four common types of printers used in labelling machines: Thermal Printers, RFID Label Printers, Inkjet Printers, and Laser Printers.
Thermal printers are widely used in labelling due to their efficiency and reliability. They apply heat to a special thermally sensitive paper, creating a clear, durable image. These printers are ideal for high-volume labelling tasks where speed is essential.
For a detailed understanding of the mechanisms behind thermal printing technology, we encourage you to read our informative article, How Does a Thermal Printer Work?
Thermal printers are of two types: direct thermal and thermal transfer printers.
For an insightful comparison between direct thermal printers and thermal transfer printers, we recommend reading our comparison guide, Direct Thermal vs Thermal Transfer Printers. This resource meticulously contrasts these two printing technologies, helping you understand their unique features and determine which is best suited for your specific printing needs.
These printers use heat-sensitive paper. The printing process involves heating the thermochromic film on the paper, which changes colour to reveal the text or image. Direct thermal printing produces monochrome results, typically black and white, but can achieve two colours by varying the temperature.
The key advantage is the absence of ink or toner, making it cost-effective and low-maintenance. However, the prints are susceptible to fading when exposed to sunlight, heat, or friction. These printers are commonly used for receipts and shipping labels.
Thermal transfer printers use a ribbon coated with solid ink, which is melted onto the substrate by the printer head. This method produces more durable prints that are less prone to fading. The substrates used can vary from paper to materials like vinyl and polyester, offering versatility. These printers are ideal for applications where label longevity is crucial.
At Triton, we pride ourselves on being the premier source for all your thermal printing requirements. Our carefully curated collection boasts industry-leading brands such as Epson, Element, Senor, Honeywell, Zebra, and TSC, as well as the vibrant colour label printers from OKI.
Tailored to meet diverse business requirements, our thermal label assortment spans from robust industrial printers to compact desktop printer models, encompassing direct thermal printers, thermal transfer printers, specialised barcode label printers, versatile mobile printers, and efficient receipt printers.
At Triton Store, we recognise that a printer is just a component of a larger ecosystem. That’s why our inventory extends beyond printers to include a wide range of accessories and top-quality thermal printheads from industry leaders such as Zebra, Honeywell, TSC, Intermec, Datamax, SATO, and Bizerba.
Our comprehensive accessory selection spans from essential spare printer parts and accessories to specialised items like waterproof printer enclosures, cables and cleaning wipes, all aimed at elevating your printing experience and ensuring consistent, superior-quality outputs.
Additionally, Triton is your source for a variety of essential thermal printer consumables, crucial for producing exceptional labels. Our product line includes thermal transfer ribbons, a variety of thermal labels, thermal carton labels, specialised thermal carcase tags, food-compliant thermal inserts, receipt rolls, and tailored shipping & freight labels.
Whether you’re revamping your existing setup or initiating a new project, Triton Store is your all-encompassing hub for thermal printing solutions. Feel free to reach out to us through the live chat widget below. Our team of experts is always eager to assist you, ensuring you receive top-notch service and support tailored to your specific needs.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) label printers combine the technology of RFID tags with standard labelling. These printers print visual information on the label and encode data into an RFID chip embedded within the label. This technology is beneficial for tracking and inventory management, allowing quick scanning and data retrieval without requiring direct line-of-sight.
RFID printers come in various models, including industrial, desktop, and mobile, to suit different labelling needs. For a comprehensive understanding of RFID printers and their applications, refer to our dedicated guide: What is an RFID printer?
Within the specialised field of RFID label printing, Triton proudly showcases state-of-the-art models, including the Zebra ZT411R, Zebra ZT231R, Honeywell PM45, and Honeywell PX4E. Each printer is meticulously engineered to integrate RFID technology into your labelling workflow effortlessly, ensuring a seamless transition and optimal performance.
Inkjet printers operate by propelling ink droplets onto the substrate, creating high-quality, detailed images.
Inkjet printers have numerous nozzles that spray microscopic ink droplets, allowing for intricate designs and a wide colour spectrum. This capability makes them suitable for labels requiring vibrant colours and detailed graphics, such as in the food and beverage industry.
While inkjet printers are cost-effective in terms of initial investment, the ongoing cost of ink is a consideration. They work well with various substrates, including glossy photo paper and textured art paper.
To compare Inkjet printers with thermal printers, refer to our Thermal Printers vs Inkjet Printers guide.
Laser printers use a laser beam to produce high-quality text and graphics on labels. The process involves a laser forming an image on a drum, which then attracts toner particles. These particles are transferred and fused onto the substrate using heat and pressure.
Laser printers are known for their speed, precision, and ability to produce durable prints resistant to UV light, heat, and friction. They are economical over time, especially for high-volume printing. However, they offer less substrate versatility than inkjet printers.
Laser printers are suitable for applications where the durability and clarity of the printed information are paramount, such as in pharmaceuticals and consumer electronics. To compare laser printers with thermal printers, refer to our Thermal Printers vs Laser Printers guide.
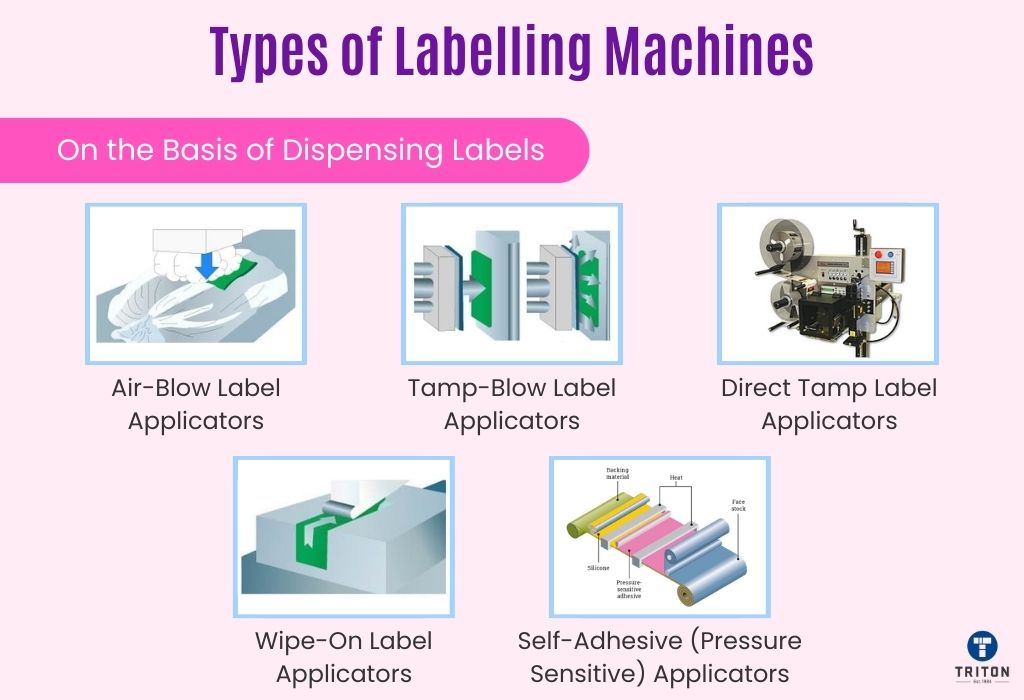
The method of dispensing labels is a crucial aspect of labelling machines, determining how labels are applied to products. Different dispensing technologies cater to various product shapes, materials, and production speeds.
Here, we explore five common types of label applicators: Air-Blow, Tamp-Blow, Direct Tamp, Wipe-On, and Self-Adhesive (Pressure Sensitive) Applicators.
Air-Blow label applicators use a burst of air to apply the label onto the product. This method is contactless, meaning the applicator does not physically touch the product.
The system incorporates a vacuum mechanism that securely holds the label before application. When the product is detected, a burst of compressed air, controlled by a pneumatic solenoid valve, propels the label onto the surface. The label, equipped with a pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA), instantly adheres to the product, ensuring a secure and accurate application.
Air-Blow label applicators are particularly useful for labelling fragile or uniquely shaped items, where traditional contact methods could result in damage or misalignment. These applicators are known for their precision and are commonly used in electronics and pharmaceutical industries.
Tamp-Blow label applicators combine air-blow and tamp technologies. Like their Air-Blow counterparts, Tamp-Blow label applicators are non-contact systems that use vacuum pressure to hold the label.
The key difference lies in using a pneumatic cylinder to move the label towards the product. This movement, combined with a blast of compressed air, allows for precise and consistent label placement without the labelling head touching the product.
Tamp-Blow applicators excel in labelling uneven surfaces, offering a balance of accuracy and gentle handling.
Direct Tamp label applicators employ a positive tamp action, pressing the label directly onto the product’s surface to create a secure bond. This method creates a strong bond between the label and the product, making it effective for rugged or uneven surfaces.
Tamp applicators are available in various sizes, including tabletop and manual versions, offering versatility for different operational scales. They are commonly used in environments where high-speed labelling is not a priority but accuracy is, such as in the case of small batch production.
Wipe-On label applicators apply labels by physically wiping them onto the product’s surface as it passes by the applicator. This system uses a roller to label products as they pass through the applicator.
The effectiveness of Wipe-On label applicators hinges on the precise synchronisation between the product’s movement and the label’s application. This synchronisation is crucial to prevent any wrinkling of labels and maintain a clean and professional appearance.
Wipe-On applicators are known for their bubble-free application and lower operating costs, as they do not require compressed air. They are efficient for high-speed labelling on flat or uniformly shaped products. They are widely used in industries with high-volume production lines, such as food and beverage or consumer goods.
Self-Adhesive applicators, also known as Pressure Sensitive applicators, use labels with a pre-applied adhesive that sticks to the product when pressure is applied. These machines are popular for their versatility and ease of use, as they require no water or heat to activate the adhesive.
Self-Adhesive applicators can handle various label sizes, shapes, and materials. They are commonly used across various industries due to their ease of use and adaptability to different production environments.
The method of attaching labels to products influences their applicability across different packaging formats. This section explores systems designed for specific label placement requirements, including Front and Back, Top and Bottom, Side, Corner, Wrap-Around, Vial, Rotary, Case Packing and Aggregation, and systems with Washdown Enclosures.
Front and Back labelling systems are designed to apply labels on both the front and back sides of a product simultaneously. These systems feature two labelling heads positioned opposite each other. As products move along the conveyor, these heads simultaneously attach labels to the front and back.
Front and Back labelling systems are highly efficient for products that require multiple labels, such as containers for food, beverages, personal care, and household products. They adapt to different container shapes (flat and rounded) and sizes, ensuring consistent label placement on both sides.
Top and Bottom labelling systems are adept at applying labels to the top and bottom surfaces of products. These systems have labelling heads positioned above and below the conveyor path. As products pass through, the labels are accurately applied to the top and bottom surfaces.
The Top and Bottom labelling system’s precise synchronisation ensures consistent label placement, making these systems suitable for various containers, including tubs, clamshells, boxes, and cartons. They are particularly favoured in the food industry for packaging that requires clear ingredient and branding information.
Side Labelling machines focus on applying labels to the side planes and arcs of products. These machines are designed for high-speed production lines. They can handle a range of product shapes and sizes, from flat-sided containers to cylindrical products.
Side Labelling machines are commonly used for labelling pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and household products, where the appearance of the label is crucial.
Corner labelling machines are tailored for applying labels to the corners of boxes or packages, a method often used for tamper-evident labelling. These machines are adept at handling both flat and side planes of boxes, making them suitable for products that require added security measures, such as electronic goods and pharmaceuticals.
For an in-depth understanding of tamper-evident labelling, refer to our dedicated guide What are Tamper Proof Labels?
Wrap-Around labelling systems are designed for cylindrical containers like bottles and cans, applying labels around the entire circumference. These systems can wrap labels fully or partially around the container, maximising the printable space.
Wrap-Around labelling systems work by spinning the product and passing it through a labelling head, which wraps the label around the container. This type of labelling is essential for products in the beverage industry, where it’s crucial to display brand information and meet UPC specifications on a single label.
Vial labelling systems focus on labelling small-diameter cylindrical containers, such as vials, commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry. These systems delicately handle the vials and apply wrap-around labels, maximising the use of the vial’s lateral surface area.
While primarily used in pharmaceuticals, Vial labelling systems also apply for labelling vials containing fragrances, oils, chemicals, and other sensitive products.
Rotary labelling systems are advanced, high-speed machines designed for precision labelling on a large scale. In these systems, products are transferred from a linear conveyor to a rotating carousel, known as the carousel. Each product is held in place on individual platforms that rotate to align with the labelling applicator.
As the product passes the applicator, it is spun to wrap the label around it. This method is ideal for applying multiple labels to different sides of a product. Rotary systems are highly synchronised and commonly used to label bottles, containers, and vials in industries like beverages, food, cosmetics, chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Labelling systems for Case Packing and Aggregation are essential in supply chain management, particularly for serialised tracking of products. These systems are used to apply labels to larger packages and cases, often as part of an aggregation process.
Aggregation involves creating a parent-child relationship among packaging levels, each receiving a unique serial number. A vision system scans each item’s serialisation. After recording all serial numbers, the items are bundled and labelled with a unique aggregate number.
Labelling systems for Case Packing and Aggregation are crucial in industries where bulk shipping and tracking are involved, providing efficient and accurate label application on cases and pallets. They also facilitate efficient processing of product recalls, returns, and damaged pallet decommissioning.
Labelling systems with Washdown Enclosures are designed for environments where cleanliness and hygiene are critical, such as in the food and beverage industry. These systems are housed in stainless steel enclosures, making them water-resistant and easy to clean.
The washdown capability ensures that the machinery can maintain functionality and hygiene standards in wet, messy, or harsh conditions.
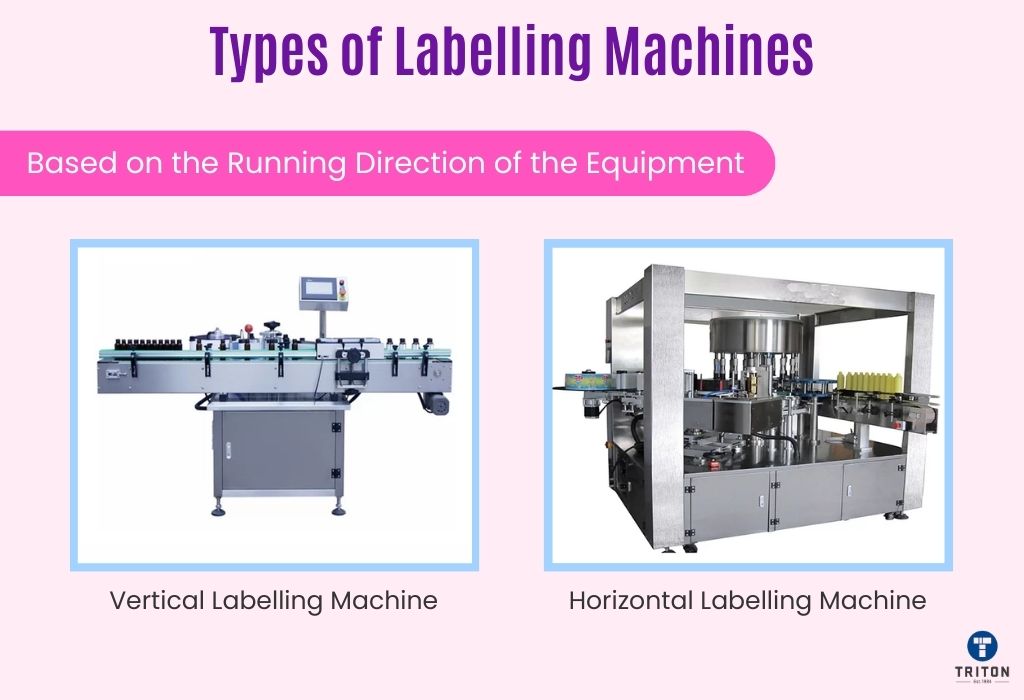
The orientation of the labelling machine, whether vertical or horizontal, plays a significant role in its operation and suitability for different types of products. This categorisation is particularly important in determining how products are fed into the machine for labelling.
Below, we explore the two main orientations: Vertical and Horizontal Labelling Machines.
Vertical labelling machines are designed for products best handled in an upright position. These machines are particularly effective for tall, slender items such as bottles, jars, and tubes.
In a vertical labelling machine, products are typically fed through the machine on a vertically oriented conveyor system. This orientation allows for precise label application on the sides of the product, and it’s especially useful for round or cylindrical items.
The vertical setup ensures stability and accurate label placement on taller items, which might be prone to tipping over in a horizontal position.
Horizontal labelling machines are ideal for more stable or effective products when laid flat. This includes items like pouches, bags, boxes, and products that are not self-standing.
In these machines, products move along a horizontal conveyor belt, and labels are applied from above, below, or the sides, depending on the machine configuration. Horizontal labelling machines are particularly well-suited for products that require top or bottom labelling and for items that need wrap-around labels applied in a continuous motion.
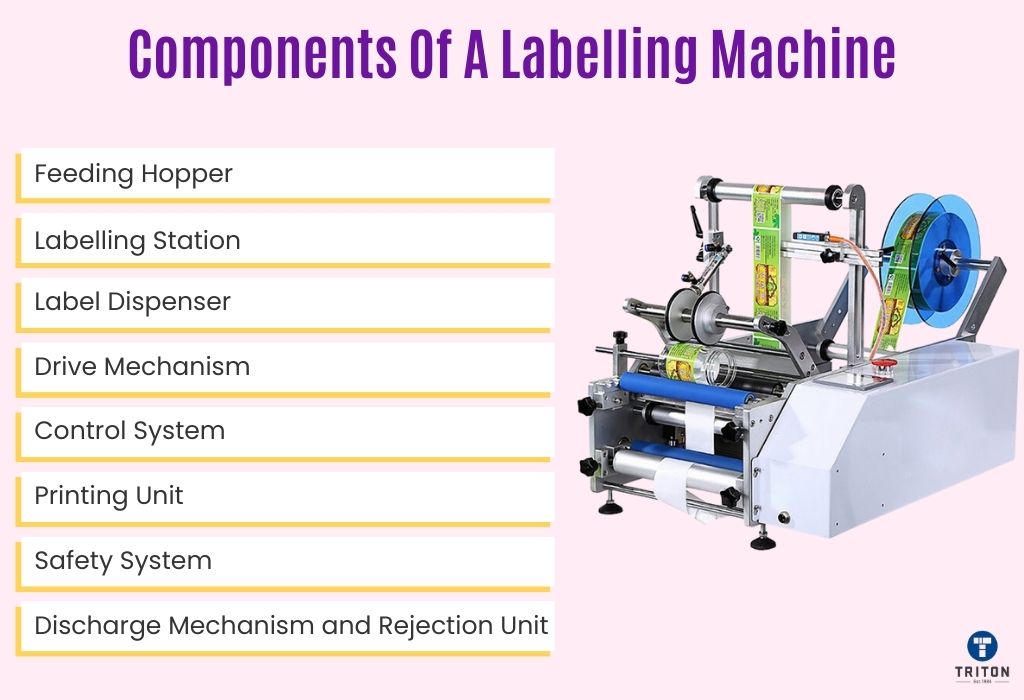
Understanding the components of a labelling machine is crucial for comprehending how these machines function. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring the efficient and accurate application of labels.
Please note that different labelling machines have varied components based on their specific functions and applications. However, there are basic components common to most machines. Here, we explore these fundamental components that facilitate the efficient operation of labelling machines.
The feeding hopper serves as the entry point for products into the labelling machine. Its primary role is to ensure a consistent and orderly supply of products into the system. This is crucial for ensuring a steady supply and uniform application of labels.
The design of the hopper is tailored to accommodate different types of products, ensuring they are correctly oriented and spaced as they move into the labelling station.
The labelling station is the heart of the machine, where labels are applied to products. This station consists of a labelling pad and a labelling head (or applicator), which work together to apply labels precisely.
The labelling pad provides a stable surface for the product during labelling, while the head is responsible for the precise application of labels. The labelling head can vary in mechanism (wipe-on brush, tamp-blow, or air-blow system) depending on the machine’s design.
The label dispenser is responsible for managing the labels in the labelling machine. It holds the label roll and peels off each label from its backing tape.
The precision of the dispenser determines the accuracy of label placement on the product. Modern dispensers have sensors to detect the label’s edge, guaranteeing consistent and accurate dispensing.
The drive mechanism powers the movement and operation of the labelling machine. It includes:
The control system is the brain of the labelling machine. It coordinates the operation of the dispenser, applicator, and conveyor. This system typically includes a user interface (like a touchscreen) for setting up and adjusting the machine’s parameters, such as label size, application speed, and label position.
In labelling machines that also print labels (print and apply machines), the printing unit is a key component. Depending on the machine, it can be a thermal, inkjet, or laser printer. This unit prints information like barcodes, batch numbers, and expiry dates on the labels before they are applied to the product.
The discharge mechanism and the rejection unit are integral to the labelling machine’s quality control system, both designed to uphold the highest standards of labelling accuracy. These components work in tandem to identify and eliminate products with defective labels or any labelling errors.
The discharge mechanism specifically targets products that fail to meet labelling criteria, ensuring they are promptly removed from the production line. Simultaneously, the rejection unit focuses on detecting and discarding errors in labels or products, safeguarding the process’s integrity. Together, they ensure that only products with perfectly applied labels progress to the next stage of production, maintaining the overall quality and reliability of the output.
The safety system includes features like emergency stop buttons and safety guards. These elements are designed to protect the operator and the machine in case of an emergency. In emergencies, activating these features immediately stops the machine, mitigating potential risks and damages.
Understanding how a labelling machine operates is essential for anyone involved in packaging or manufacturing or those simply curious about the process. Despite the variety of labelling machines available, they all follow a fundamental sequence of operations to apply labels to products. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a typical labelling machine works:
The process begins with the feeding of products into the labelling machine. Products are manually or automatically loaded into the feeding hopper, which then systematically supplies the products into the machine.
The hopper ensures that products are correctly oriented and spaced as they move towards the labelling station.
As products enter the labelling station, the label dispenser activates. This component holds a roll of labels and peels each label from its backing tape. Modern label dispensers are equipped with sensors that detect the edge of each label, ensuring that labels are dispensed at precise intervals. This precision is crucial for aligning the labels with the products.
At the labelling station, the dispensed label is applied to the product. This can be achieved through various mechanisms, depending on the type of labelling machine.
After application, the label needs to adhere properly to the product. This is typically achieved through pressure or heat, ensuring the label sticks firmly and smoothly.
For self-adhesive labels, pressure from the applicator is sufficient.
For labels requiring heat activation (like certain shrink labels), the product may pass through a heat tunnel after label application.
Many labelling machines include a quality control mechanism, such as sensors or cameras, to verify the label’s position and presence. If a product is incorrectly labelled or misses a label, it can be rejected or removed from the line through a discharge mechanism. This step is crucial for maintaining high standards of product presentation and compliance.
Finally, the labelled products are discharged from the machine and ready for the next step in the production line, whether it be packaging, shipping, or further processing. The discharge mechanism ensures that products are smoothly transitioned out of the labelling machine without damage or disruption to the labels.
Throughout the process, the machine’s control system oversees the operation, allowing adjustments to be made for different product types, label sizes, and application speeds. The safety system ensures that the machine operates safely, with emergency stops and protective measures in place to protect both the operator and the machinery.
Labelling machines have become indispensable in various industries, from food and beverage to pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. Their integration into production lines offers numerous benefits, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and product presentation.
Here are some key benefits of using labelling machines.
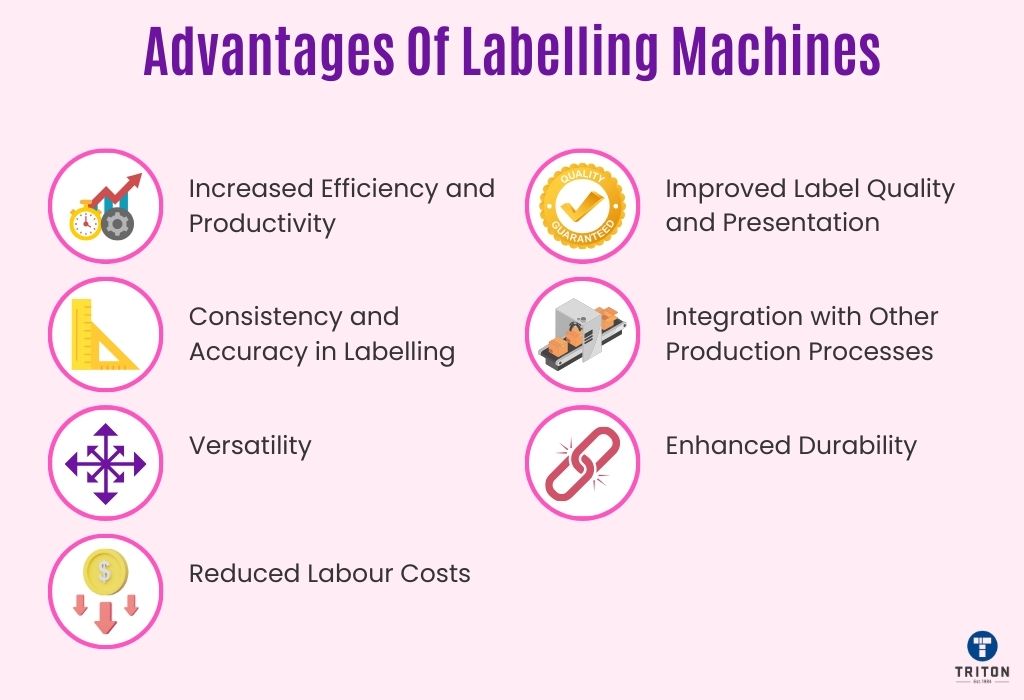
Labelling machines automate the process of applying labels, significantly speeding up production rates compared to manual labelling. They can operate continuously for extended periods, handling high volumes of products with consistent speed, directly translating to increased productivity and the ability to meet higher demand.
One of the most significant advantages of labelling machines is their ability to apply labels consistently and accurately. These machines ensure that labels are placed in the exact same position on every product, maintaining uniformity that is challenging to achieve manually. Such consistency is crucial for the brand image and compliance with regulatory labelling requirements.
For businesses in the food and beverage sector seeking guidance, our articles’ Country of Origin Labelling in Australia‘ and ‘Labelling of Alcoholic Beverages in Australia’ provide invaluable insights and information to navigate these regulations effectively.
Modern labelling machines are designed to handle a wide range of product shapes, sizes, and types, as well as various label materials and designs. With adjustable settings and interchangeable parts, one machine can accommodate different labelling needs, making them versatile tools for companies with diverse product lines.
By automating the labelling process, companies can significantly reduce the labour costs associated with manual labelling. This includes the direct cost of labour and the potential costs related to human error, such as wasted materials and rework. Labelling machines require minimal supervision, allowing staff to focus on other productive tasks.
Labelling machines apply labels smoothly and without wrinkles or bubbles, enhancing the product’s aesthetic appeal. High-quality label application is essential for attracting customers, especially in competitive retail environments where product presentation can influence purchasing decisions.
Labelling machines can be easily integrated with other production line processes, such as filling, capping, and packaging. This integration streamlines the production process, reducing the time and effort required to manage different stages of product packaging.
With proper maintenance, labelling machines can easily serve a production line for more than 10 years, demonstrating remarkable durability. This long-term reliability makes them a wise investment for any business looking to ensure consistent labelling quality over time.
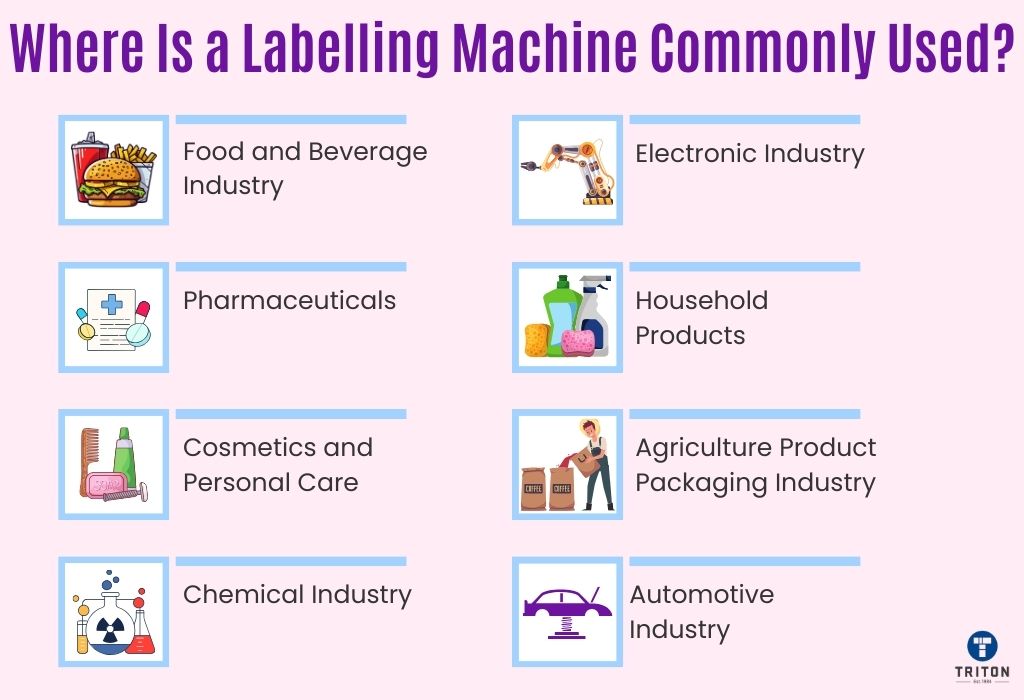
Labelling machines are versatile tools essential in various industries for enhancing product presentation, ensuring compliance, and improving efficiency. Here are some key sectors where they are commonly used:
Labelling machines offer a blend of efficiency, accuracy, and versatility that manual labelling processes simply cannot match. These machines adeptly handle a wide array of product types and materials, ensuring that every item is accurately labelled according to industry standards.
Labelling machines significantly enhance operational productivity by integrating into an existing production line or serving as a standalone solution. As technology advances, the future of labelling machines promises even greater adaptability and precision, further solidifying their role as an indispensable asset in the manufacturing and packaging sectors.
We hope this article was useful. Thanks for reading!
Yes, labelling is necessary for several reasons. It provides essential information to consumers, including product usage, ingredients, and safety warnings. Labelling is also critical in branding and marketing, helping products stand out on shelves. Furthermore, in many industries, regulations mandate labelling to ensure consumer safety and product traceability.
Take the chemical industry, for instance, which must adhere to the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). For those involved in chemical labelling, the following guides are essential tools to ensure compliance and enhance safety:
Labelling machines are designed to handle various surface types and materials, making them versatile for various applications. Here are some examples:
Almost any product can be labelled using a labelling machine, thanks to the versatility and range of machines available. However, the specific type of labelling machine required depends on the product’s shape, size, material, and label placement.
The cost of a labelling machine varies widely based on its type, capabilities, and level of automation. Basic manual labelling machines can cost a few hundred dollars, while high-speed, fully automated systems may cost tens of thousands.
The investment in a labelling machine should be considered based on the specific needs of the production line, potential ROI, and efficiency improvements.
Yes, labelling machines can be integrated into existing production or packaging lines. Most modern labelling machines are designed with flexibility in mind and can be customised to fit within current operations. Integration may involve configuring the machine to match the line’s speed, product handling, and space requirements.
Melbourne
Brisbane
Phone 1300 558 438
Live Chat – Widget below
Melbourne
Brisbane
Phone 1300 558 438
Live Chat – Widget below