QR codes were developed in 1994 by Denso Wave, a subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation. They were initially developed to track automobile parts.
The popularity of the QR code system was fueled by the introduction of mobile phones equipped with QR code-reading capabilities. With a simple scan using their mobile devices, individuals gained access to websites, exclusive offers, and valuable content linked to the QR codes.
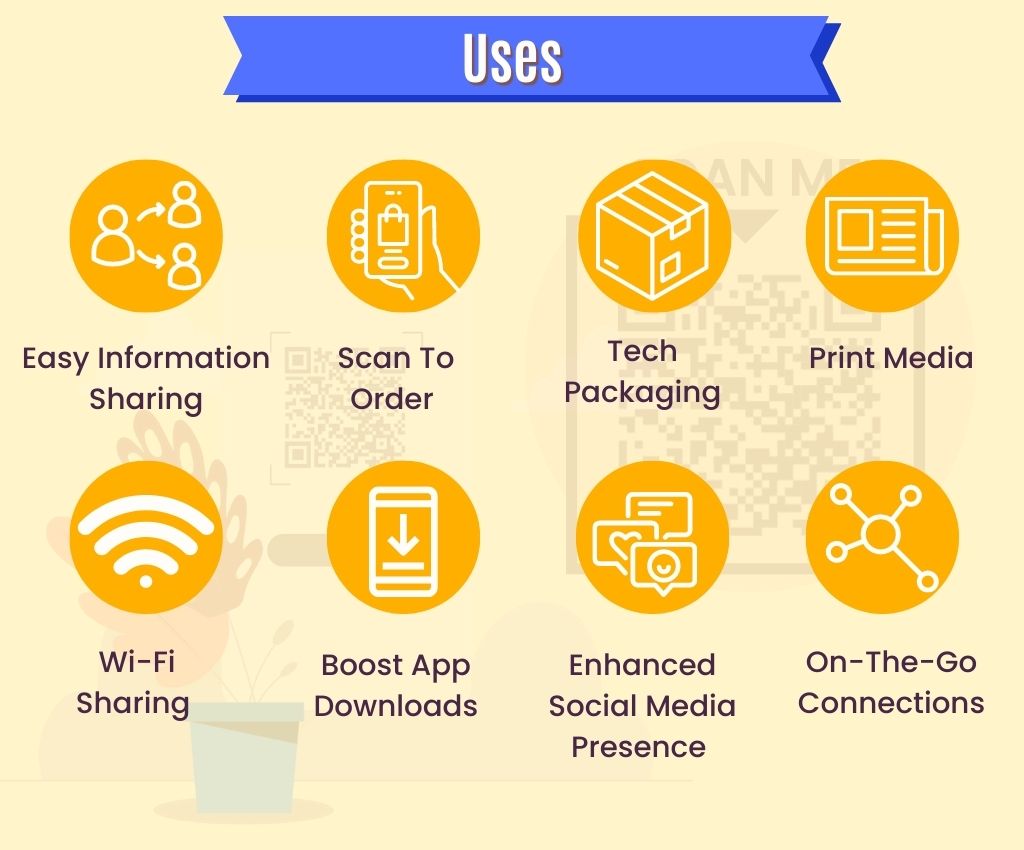
Nowadays, QR codes have become crucial for businesses and individuals, serving various purposes such as contactless payments, electronic tickets, name cards, marketing campaigns and other similar uses.
Although QR codes have been around for decades, their usage has significantly increased due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This fact is confirmed by a report published by Statista, which reveals that in the United States alone, the number of households that scanned QR codes in 2020 was 11 million – a notable rise from 9.76 million scans in 2018.
Such increased numbers of QR Code scanning can be accredited to the growing trend of contactless transactions as a safety measure during the pandemic. The trend continued to rise as the number of QR codes scanned amounted to 89 million in 2022, indicating a 26% increase compared to the previous year. These statistics are a testament to the importance of QR codes in our modern world.
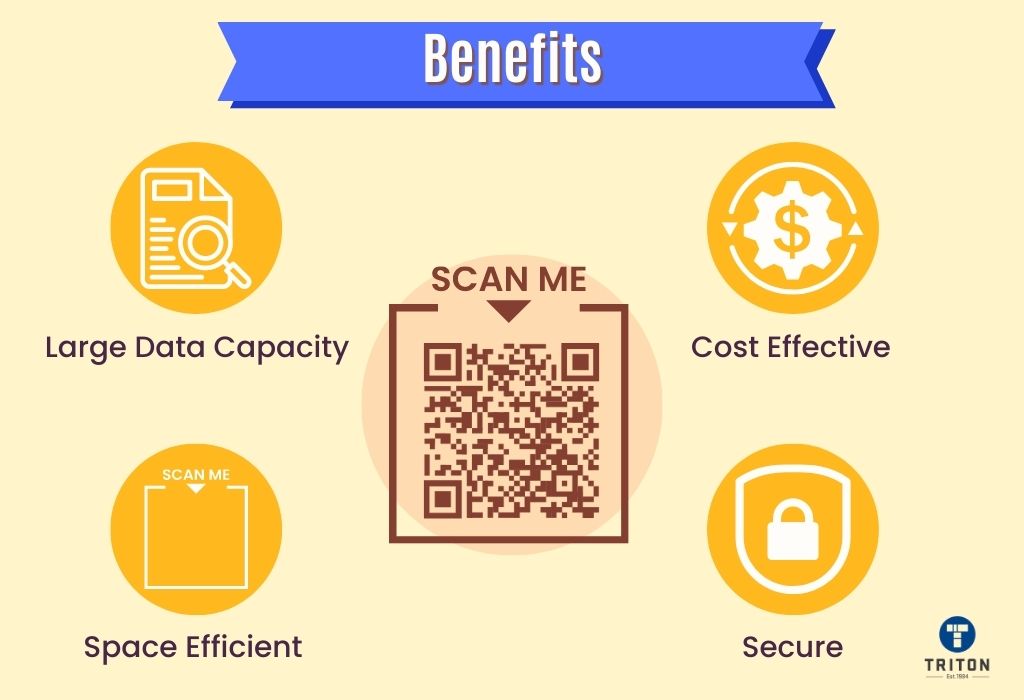
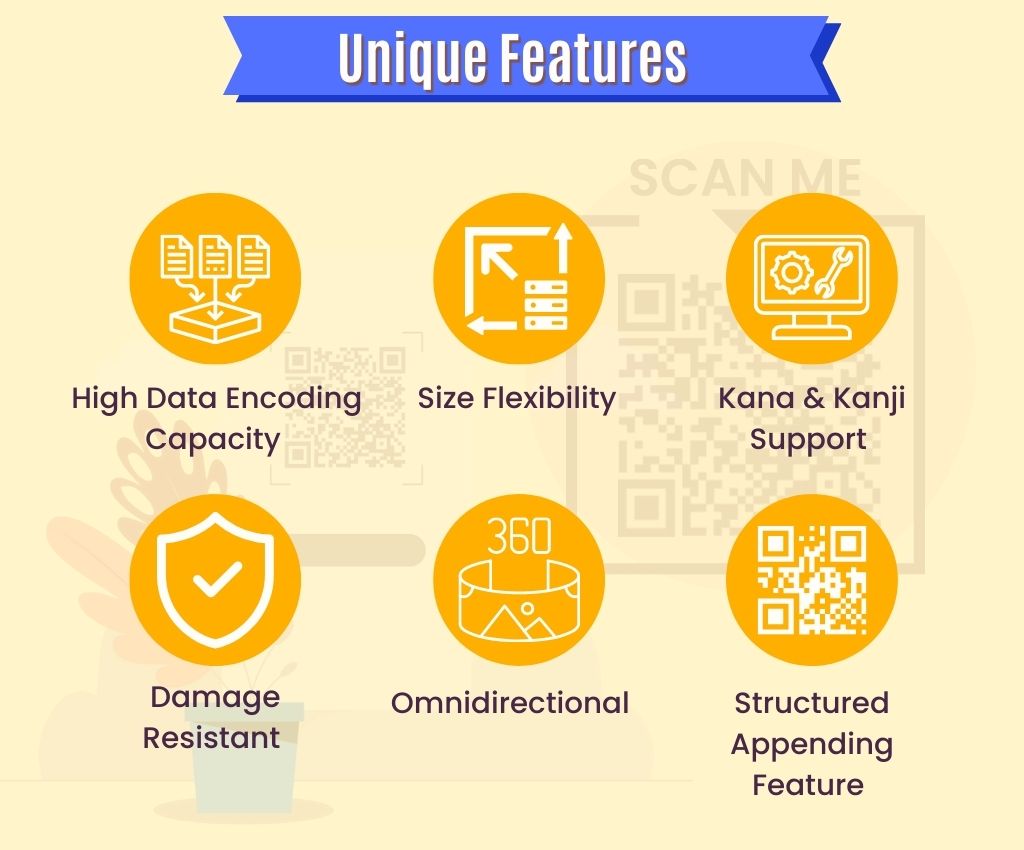
A QR code can hold up to 2953 bytes of data, 4296 alphanumeric characters, 7089 numeric characters, or 1817 Kanji characters (a character set according to JIS X 0208). This makes QR codes suitable for providing links to websites or applications and multimedia content such as images, videos and audio files.
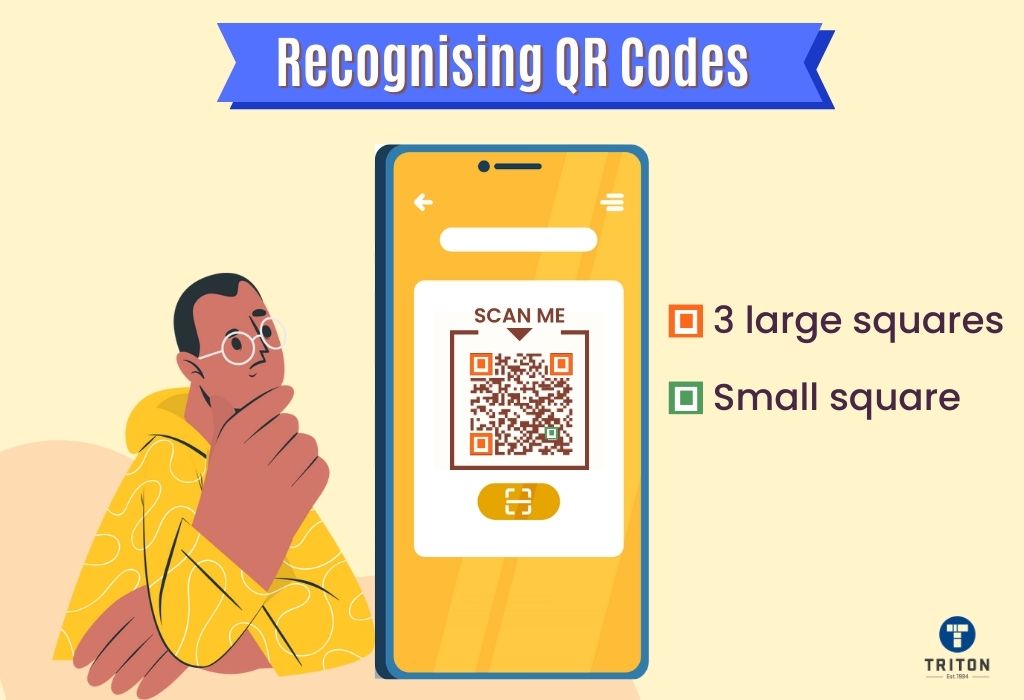
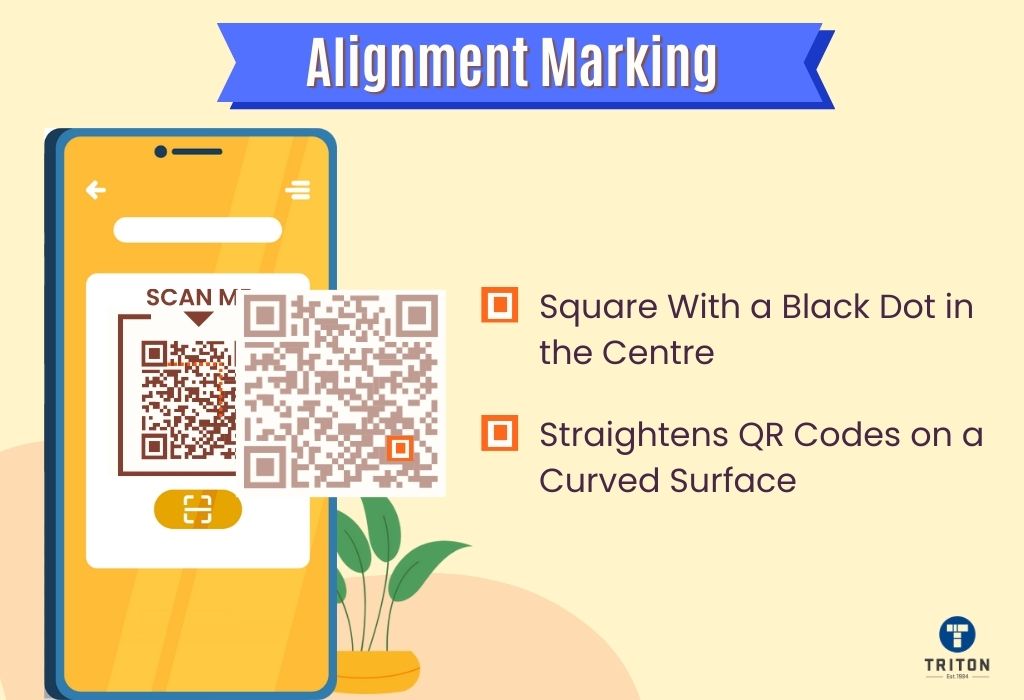
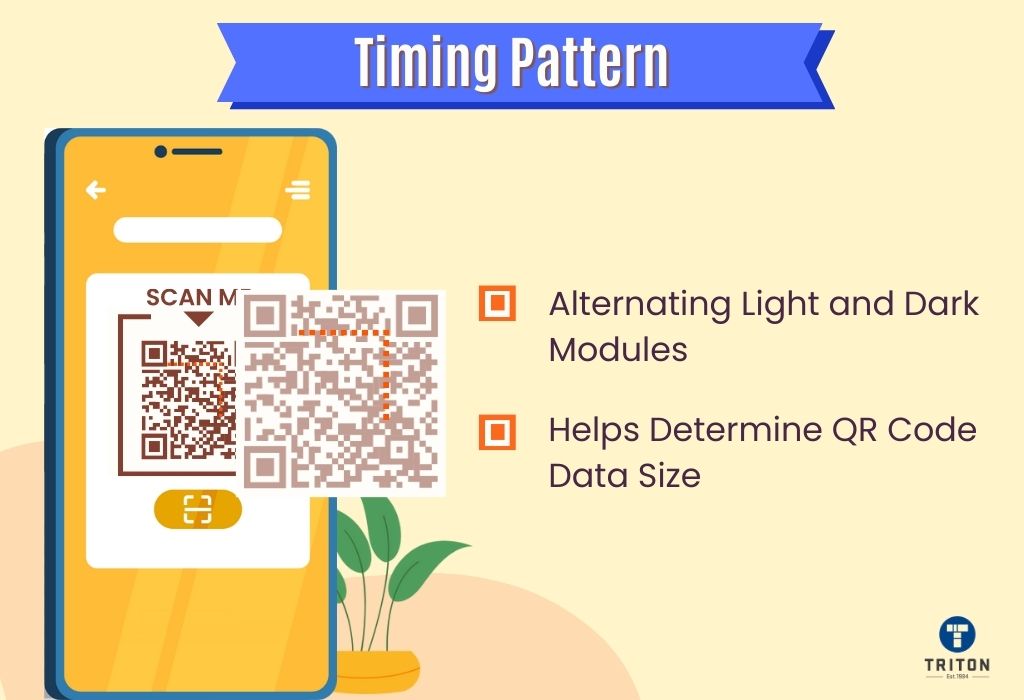
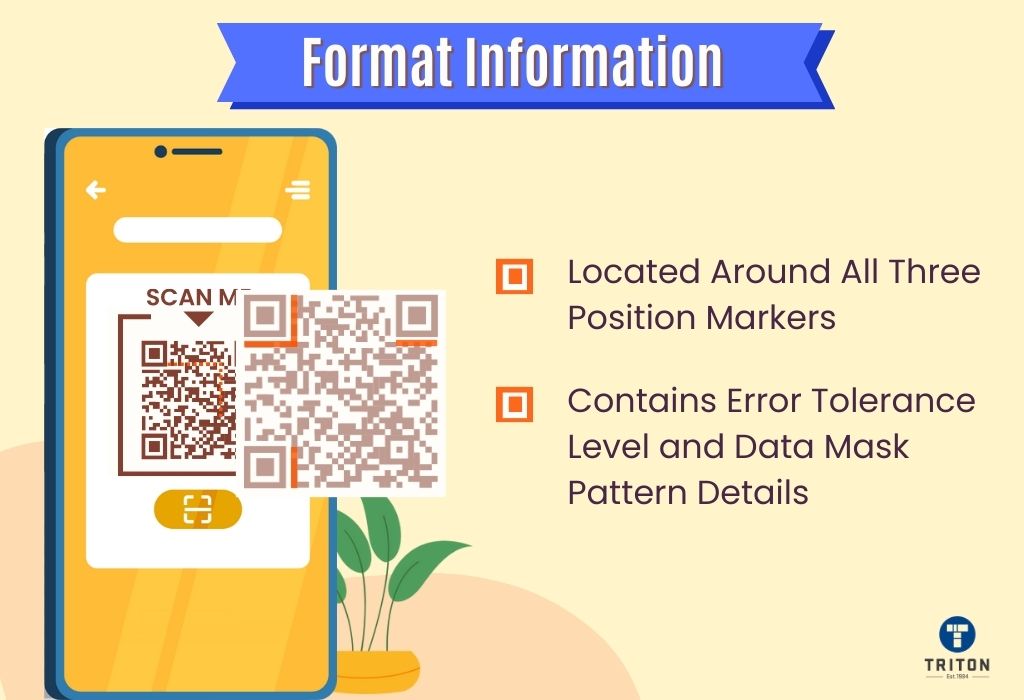
Compared to traditional barcodes, QR codes offer several benefits. They can be scanned using camera-enabled devices like smartphones without additional hardware. Additionally, QR codes can be scanned from any angle and have error correction abilities and size flexibility.
QR Codes provide a convenient way for businesses and customers to access information quickly and securely. Their ease of use makes them popular among marketers and customers alike, as they can transfer large amounts of data in a single scan with minimal effort.