
Digital printing is a printing method that prints digital files on materials such as paper, canvas, and fabric, using ink or toner using digital printers. This process removes the need for printing plates, resulting in a quicker setup and more adaptable production.
So, how is digital printing different from offset printing?
Offset printing uses metal plates to print images, whereas digital printing works from digital files like PDFs, using software and drivers to convert the file for printing. The output is comparable to offset printing, but the process is simpler and more efficient.
Digital printing is more efficient because it reduces setup time by eliminating the need for designing, creating, and aligning printing plates. It also allows for on-demand printing, meaning smaller runs can be produced without the waste associated with traditional methods.
Changes or corrections to the design are also easier in digital printing.
This article will explain how digital printing works, its types, and the benefits it provides over traditional methods.
The digital printing process begins with the creation of a file, which can include text, images, or both.
Digital files are processed in two different ways before they are printed.
The file processing depends on the artwork and the capabilities of the digital printer. Popular file formats in digital printing include PDF, TIFF, JPEG, and EPS.
Raster images use a matrix of pixels while vector graphics use mathematical formulas to represent the image. Raster images cannot be scaled while vector images can (theoretically) be scaled indefinitely.
The process of preparing the file for printing, known as Raster Image Processing (RIPping), involves converting the file (if needed), managing colour separations, adjusting resolution, and ensuring proper alignment. RIP software plays a critical role in controlling how ink or toner is applied to the material.
Once the file is processed, the digital printer uses the data to guide the printing process. There are many digital printing technologies, including laser, inkjet, dye sublimation, and UV printing.
After printing, materials often go through finishing processes such as cutting, folding, laminating, or binding to create the final product. These steps are essential for products like packaging, brochures, and promotional materials.
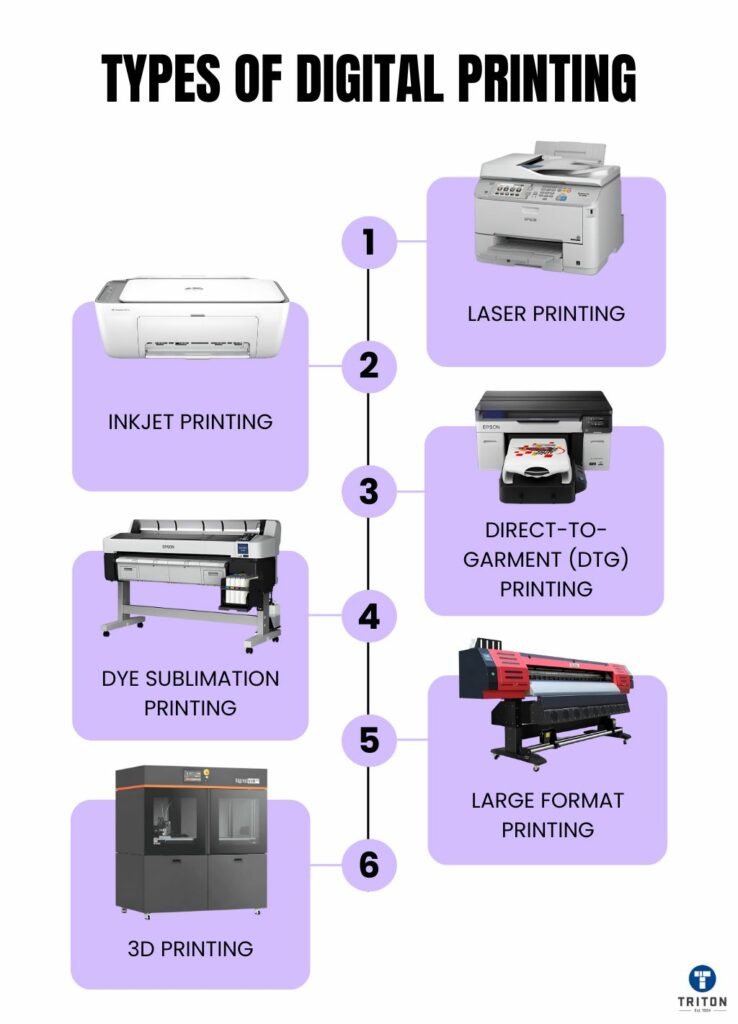
Types of Digital Printing | Where They Are Used |
|---|---|
Laser Printing | Office reports, invoices, brochures, flyers, high-volume black-and-white documents, and labels. Suitable for corporate settings and printing on thick cardstock. |
Inkjet Printing | High-quality photo books, fine art, posters, and vinyl banners. Also used for printing on various materials such as photo paper, canvas, fabric, and synthetics. |
Direct-to-Garment (DTG) Printing | Custom t-shirts, hoodies, and boutique clothing, primarily printed on cotton or cotton-blend fabrics. Best for small runs and requires pre-treatment for dark fabrics. |
Dye-Sublimation Printing | Custom mugs, mouse pads, sportswear, and promotional products. Only suitable for polyester fabrics and polymer-coated surfaces.
|
Large Format Printing | Billboards, trade show banners, vehicle wraps, wall murals, floor graphics, and architectural blueprints printed on materials such as vinyl and fabric. |
Let’s look at the advantages of digital printing which makes it popular for a wire variety of printing requirements in businesses of all sizes.
High Output and Duty Cycle: Digital printing presses are built to handle large workloads. The Xerox Iridesse has a monthly duty cycle of up to 2,250,000 impressions, making it perfect for high-volume commercial printing. HP Indigo presses, with their Enhanced Productivity Mode, can increase throughput by 33% while reducing energy consumption, ensuring businesses can handle large-scale print campaigns without sacrificing quality.
Digital printing has redefined how businesses manage their printing tasks. With its combination of speed, precision, and versatility, it allows for efficient production across a wide range of media with ultra-detailed quality. Whether you need small custom runs or large-scale prints, digital printing meets the demands of today’s fast-paced environments. Its flexibility also reduces waste and streamlines workflows, making it a sustainable choice for modern businesses.
To find the perfect printer for your office or industrial needs, explore the Triton Store at tritonstore.com.au and discover the best selection of thermal printers here.
Melbourne
Brisbane
Phone 1300 558 438
Live Chat – Widget below
Melbourne
Brisbane
Phone 1300 558 438
Live Chat – Widget below